 简单工厂
简单工厂
# 简单工厂(Simple Factory)
# Intent
在创建一个对象时不向客户暴露内部细节,并提供一个创建对象的通用接口。
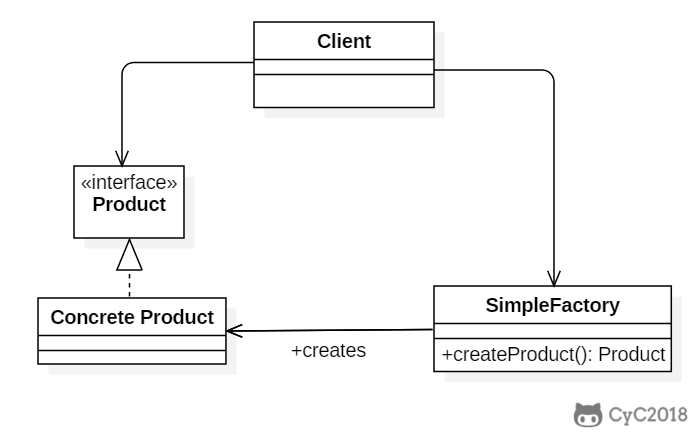
# Class Diagram
简单工厂把实例化的操作单独放到一个类中,这个类就成为简单工厂类,让简单工厂类来决定应该用哪个具体子类来实例化。
这样做能把客户类和具体子类的实现解耦,客户类不再需要知道有哪些子类以及应当实例化哪个子类。客户类往往有多个,如果不使用简单工厂,那么所有的客户类都要知道所有子类的细节。而且一旦子类发生改变,例如增加子类,那么所有的客户类都要进行修改。
# Implementation
package com.code.factory.example2;
public interface Product {
void onProduct();
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
package com.code.factory.example2;
public class CommonProduct1 implements Product {
public void onProduct() {
System.out.println(toString() + " : CommonProduct1");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
package com.code.factory.example2;
public class CommonProduct2 implements Product {
public void onProduct() {
System.out.println(toString() + " : CommonProduct2");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
package com.code.factory.example2;
public class CommonProduct3 implements Product {
public void onProduct() {
System.out.println(toString() + " : CommonProduct3");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
以下的 SimpleFactory 是简单工厂实现,它被所有需要进行实例化的客户类调用。
package com.code.factory.example2;
public class SimpleFactory {
public Product createProduct(int type) {
if (type == 1) {
return new CommonProduct1();
} else if (type == 2) {
return new CommonProduct2();
}
return new CommonProduct3();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
以下的 Main 类包含了实例化的代码。
package com.code.factory.example2;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleFactory simpleFactory = new SimpleFactory();
Product product = simpleFactory.createProduct(1);
product.onProduct();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
com.code.factory.example2.CommonProduct1@1c4af82c : CommonProduct1
1