 设计模式 - 享元
设计模式 - 享元
# 享元(Flyweight)
# Intent
利用共享的方式来支持大量细粒度的对象,这些对象一部分内部状态是相同的。
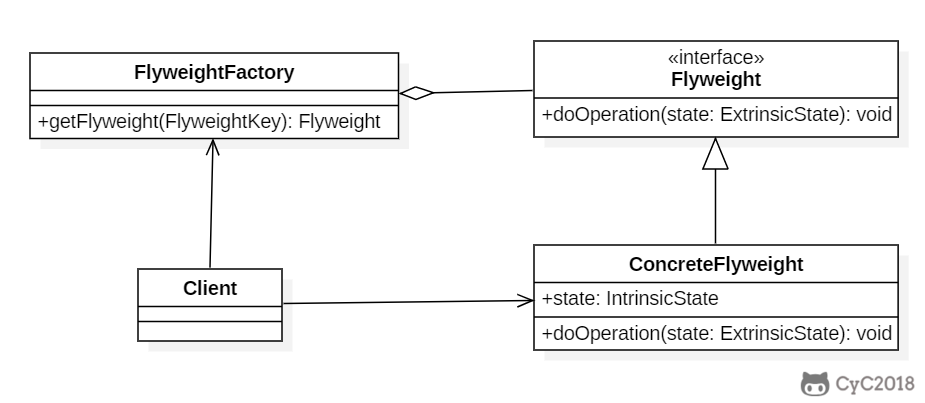
# Class Diagram
- Flyweight:享元对象
- IntrinsicState:内部状态,享元对象共享内部状态
- ExtrinsicState:外部状态,每个享元对象的外部状态不同
# Implementation
package com.code.structural.example3;
public interface Flyweight {
void doOperation(String extrinsicState);
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
package com.code.structural.example3;
public class ConcreteFlyweight implements Flyweight {
private String intrinsicState;
public ConcreteFlyweight(String intrinsicState) {
this.intrinsicState = intrinsicState;
}
@Override
public void doOperation(String extrinsicState) {
System.out.println("Object address: " + System.identityHashCode(this));
System.out.println("IntrinsicState: " + intrinsicState);
System.out.println("ExtrinsicState: " + extrinsicState);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
package com.code.structural.example3;
public class FlyweightFactory {
private HashMap<String, Flyweight> flyweights = new HashMap<>();
Flyweight getFlyweight(String intrinsicState) {
if (!flyweights.containsKey(intrinsicState)) {
Flyweight flyweight = new ConcreteFlyweight(intrinsicState);
flyweights.put(intrinsicState, flyweight);
}
return flyweights.get(intrinsicState);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
package com.code.structural.example3;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FlyweightFactory factory = new FlyweightFactory();
Flyweight flyweight1 = factory.getFlyweight("aa");
Flyweight flyweight2 = factory.getFlyweight("aa");
flyweight1.doOperation("x");
flyweight2.doOperation("y");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Object address: 1163157884
IntrinsicState: aa
ExtrinsicState: x
Object address: 1163157884
IntrinsicState: aa
ExtrinsicState: y
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
# JDK
Java 利用缓存来加速大量小对象的访问时间。
- java.lang.Integer#valueOf(int)
- java.lang.Boolean#valueOf(boolean)
- java.lang.Byte#valueOf(byte)
- java.lang.Character#valueOf(char)